مخطط الموضوع
عام
Welcome to History of Economic Facts! 🎓

Dear Students,
Welcome to the History of Economic Facts module for Second-Year Bachelor's students in Economic Sciences for the academic year 2025/2026.
🌟 What Will You Learn?
This course will take you on a journey through major economic events from the 1929 Great Depression to the 2008 Global Financial Crisis. You will:
✨ Understand key economic events that shaped our modern world
✨ Analyze the causes and consequences of economic crises
✨ Explore the development of economic systems (capitalism vs. socialism)
✨ Learn about economic globalization and international organizations
✨ Develop critical thinking about current economic challenges
📚 Course Information:
- Instructor: Dr. Hassiba Almi, Assistant Professor (Grade B)
- Weekly Hours: 3 hours (1.5h Lecture + 1.5h Tutorial)
- Credits: 4 | Coefficient: 2
- Class Time: Wednesday, 13:30 – 15:00, Lecture Hall 6
📧 Contact:
- Email: hassibaali090@gmail.com
- Office: Office N°47 Economic Sciences Department
💪 Assessment Breakdown:
- Final Exam: 60%
- Continuous Assessment: 40%
- Midterm Exam: 10%
- Research Assignment: 12%
- Individual Project: 2%
- Attendance: 12%
- Class Participation: 4%
✅ Get Started Now:
- Download and read the syllabus
- Review the course calendar
- Join the discussion forum
- Attend the first lecture
Let's make this semester a rewarding learning experience!
Dr. Hassiba Almi 📅 First Lecture: September 24, 2025
📄 Syllabus
Dear Students,
📥 Download and read this syllabus carefully before the first class.
✅ Course objectives and weekly schedule
✅ Grading system and assignments
✅ Important dates and deadlines
✅ Course requirements and policies⚠️ Action Required:
After reading the syllabus, you must sign the acknowledgment form during tutorial sessions to confirm that you:
✓ Have read and understood the syllabus
✓ Agree to the course requirements
✓ Commit to attendance and participation📝 Signature required in tutorials
📧 Questions? hassibali090@gmail.com
"Read it. Understand it. Sign it. Succeed!" 🎓✨
📢 Communication Space
Welcome to the Discussion Forum – History of Economic Facts
Dear Students,
Welcome to the official forum of our History of Economic Facts course (Semester 3 – 2nd Year, Economic Sciences).
This space is designed to foster collaborative learning, discussion, and knowledge sharing. Here, you can:
✅ Ask questions related to lectures, concepts, and weekly topics
✅ Share your ideas and reflections on economic events
✅ Engage in peer-to-peer learning and support each other
✅ Discuss assignments, projects, and research papers
✅ Share interesting articles, videos, or resources about economic history
✅ Receive announcements and responses from your instructor
📌 Forum Guidelines
✔️ Be respectful and constructive in your comments
✔️ Title your messages clearly (e.g., "Question about the 1929 Great Depression")
✔️ Search before posting – someone may have already asked your question
✔️ Keep messages relevant to course material
✔️ Write in English to practice and benefit everyone
✔️ Support your classmates – help create a collaborative learning community💬 First Discussion Question:
"Which economic event in history interests you most, and why?"
Reply to this thread and share your thoughts in a few sentences!
Looking forward to a semester full of learning, critical thinking, and historical discovery!
Warm regards,
Dr. Hassiba Almi
📧 hassibali090@gmail.comImportant Announcement for History of Economic Facts Students
Dear Students,
Interactive live sessions will be held via Google Meet to discuss course topics, review key concepts, and answer your questions.
📅 Date and Time: Every Thursday, 17:00 - 18:30.
🔗 Join Link: https://meet.google.com/yzm-uqcp-mxc💡 What to Expect:
- Review of weekly topics
- Q&A sessions
- Discussion of assignments
- Exam preparation support
This is an excellent opportunity for direct interaction. We look forward to your active participation!
📧 Questions? hassibali090@gmail.com
🎯 Learning Objectives
General Objective of This Module:
This course enables students to perceive and comprehend economic facts within their historical context, from the 1929 Great Depression up to the Global Financial Crisis of 2008.

Upon Successful Completion of This Course, Students Should Be Able To:
✓ Understand and explain the significance of major economic events in history
✓ Analyze the causes and consequences of economic crises (1929 and 2008)
✓ Compare socialist and capitalist economic systems after World War II
✓ Evaluate the impact of the Industrial Revolution on Europe and the world
✓ Explain the Bretton Woods system and the new world economic order
✓ Discuss the collapse of the Soviet Union and its economic implications
✓ Identify factors behind the rise of Asian economies
✓ Understand economic globalization and the role of international blocs
✓ Apply historical knowledge to analyze current economic challenges
📚 Course Units
Welcome to History of Economic Facts!
This comprehensive module is designed to guide you through major economic events that shaped our modern world, from the 1929 Great Depression to the 2008 Global Financial Crisis. Each unit is structured to provide clear, historical insights and build your understanding progressively of how economic systems evolved and transformed societies.
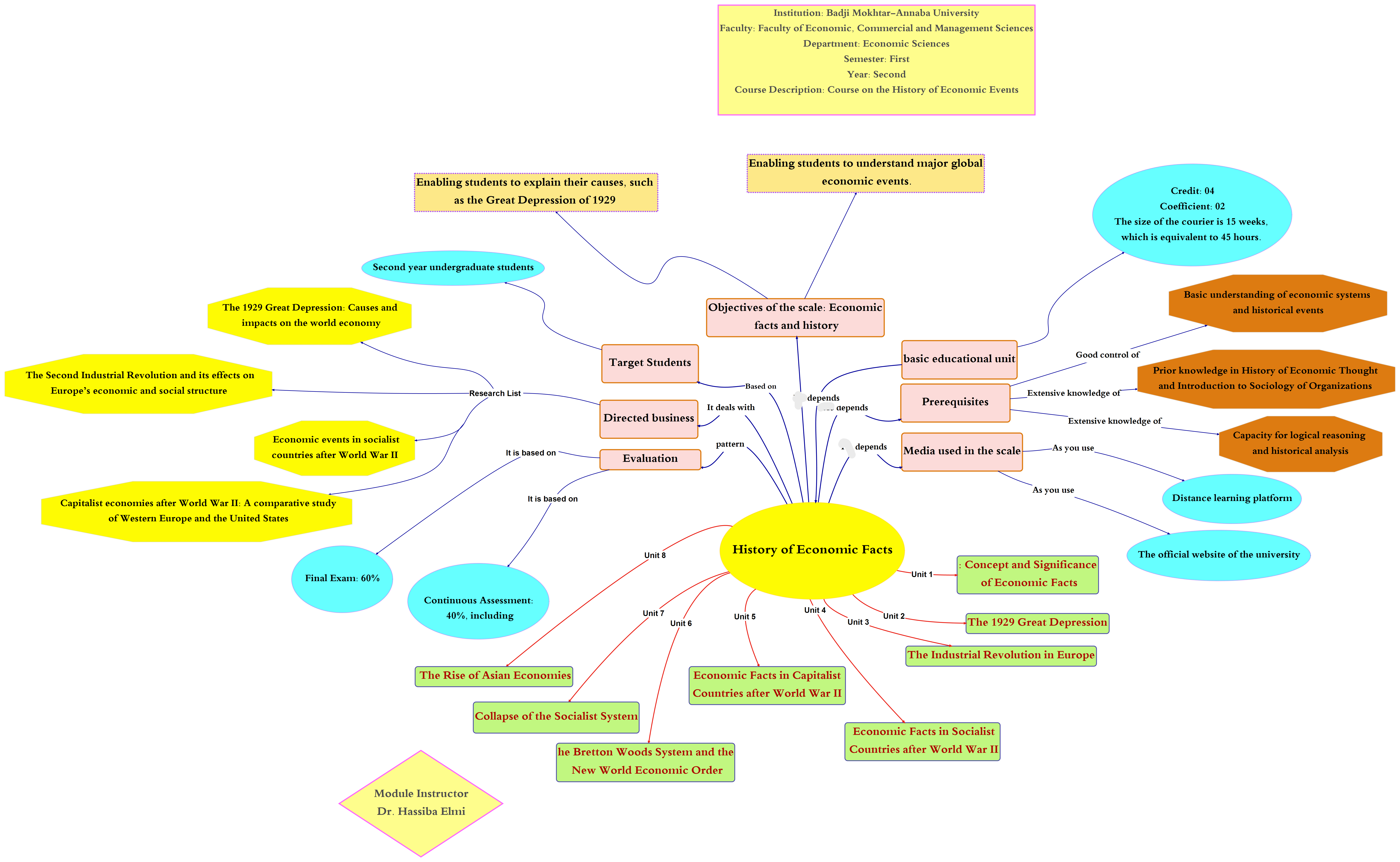
📘 Unit 1: Concept and Significance of Economic Facts
This foundational unit introduces you to the study of economic history and its importance in understanding today's economy.
What You'll Learn:
- Definition: Understanding what economic facts are and why they matter
- Historical Method: How economists study and analyze historical economic events
- Significance: The role of economic history in understanding current economic challenges
- Analytical Framework: Tools for examining economic events in their historical context
📘 Unit 2: The 1929 Great Depression
This unit explores one of the most devastating economic crises in modern history and its global impact.
What You'll Learn:
- Causes: Stock market speculation, banking failures, and economic policies
- The Wall Street Crash: Events of October 1929 and immediate consequences
- Global Spread: How the crisis affected countries worldwide
- Social Impact: Unemployment, poverty, and social upheaval
- Initial Responses: Government attempts to address the crisis
📘 Unit 3: The 1929 Great Depression (Continued)
Continuing our exploration of the Great Depression, this unit focuses on recovery efforts and long-term impacts.
What You'll Learn:
- New Deal Policies: Roosevelt's programs to revive the American economy
- International Responses: How different countries addressed the crisis
- Recovery Process: The path from depression to economic stability
- Lessons Learned: Economic theories and policies that emerged from the crisis
📘 Unit 4: The Industrial Revolution in Europe
This unit examines the transformation of European economies through industrialization in the 18th and 19th centuries.
What You'll Learn:
- Origins: Preconditions and factors that led to industrialization
- Technological Innovations: Steam engine, mechanization, and factory system
- Economic Transformation: From agrarian to industrial economies
- Geographic Spread: How industrialization spread across Europe
- Key Industries: Textiles, coal, iron, and railways
📘 Unit 5: The Industrial Revolution in Europe (Continued)
This unit explores the broader social and economic impacts of the Industrial Revolution.
What You'll Learn:
- Social Changes: Urbanization, class formation, and labor movements
- Economic Systems: Rise of industrial capitalism
- Living Conditions: Impact on workers and families
- Global Impact: How European industrialization affected the world economy
📘 Unit 6: Economic Facts in Socialist Countries after World War II
This unit examines economic systems and development in socialist countries during the Cold War era.
What You'll Learn:
- Soviet Economic Model: Central planning and command economy principles
- Collectivization: Agricultural and industrial organization
- Economic Performance: Achievements and challenges of planned economies
- Eastern Europe: Socialist economies in the Soviet bloc
- Economic Strategies: Five-year plans and industrialization drives
📘 Unit 7: Economic Facts in Capitalist Countries after World War II
This unit explores economic development and prosperity in Western capitalist countries after 1945.
What You'll Learn:
- Post-War Reconstruction: Rebuilding Europe and Japan
- Marshall Plan: American aid and its economic impact
- Economic Boom: The "Golden Age" of capitalism (1945-1973)
- Welfare State: Development of social security systems
- Comparative Analysis: Capitalism vs. Socialism in practice
📘 Unit 8: The Bretton Woods System and the New World Economic Order
This unit examines the international monetary system established after World War II and its evolution.
What You'll Learn:
- Bretton Woods Conference (1944): Creation of a new international economic order
- International Institutions: IMF, World Bank, and their roles
- Fixed Exchange Rates: The dollar-gold standard system
- Global Trade: GATT and trade liberalization
- System Operation: How Bretton Woods functioned (1945-1971)
📘 Unit 9: The Bretton Woods System (Continued)
This unit explores the collapse of Bretton Woods and the transition to a new economic era.
What You'll Learn:
- System Breakdown: Factors leading to collapse (1971)
- Nixon Shock: End of dollar-gold convertibility
- Floating Exchange Rates: New international monetary system
- Oil Crises (1973, 1979): Impact on global economy
- Stagflation: Economic challenges of the 1970s
📘 Unit 10: The Collapse of the Socialist System (Fall of the Soviet Union)
This unit analyzes the economic factors behind the collapse of socialism in Eastern Europe and the USSR.
What You'll Learn:
- Economic Stagnation: Problems in the Soviet economy (1970s-1980s)
- Reform Attempts: Perestroika and Glasnost under Gorbachev
- Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989): Symbol of communism's collapse
- Soviet Dissolution (1991): End of the USSR
- Transition to Market Economy: Challenges and outcomes
📘 Unit 11: The Rise of Asian Economies
This unit explores the remarkable economic growth of Asian countries in the late 20th century.
What You'll Learn:
- Japan's Economic Miracle: Post-war recovery and rapid growth
- Asian Tigers: South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore, and Hong Kong
- China's Economic Reforms: Deng Xiaoping's "opening up" (1978)
- Export-Led Growth: Development strategies and industrialization
- Regional Integration: ASEAN and Asian economic cooperation
📘 Unit 12: Economic Globalization and International Blocs
This unit examines the process of economic integration and formation of regional trading blocs.
What You'll Learn:
- Globalization Process: Trade liberalization and capital flows
- Regional Blocs: EU, NAFTA, ASEAN, MERCOSUR
- Multinational Corporations: Role in global economy
- World Trade Organization (WTO): Global trade governance
- Digital Economy: Technology's impact on globalization
📘 Unit 13: Economic Globalization (Continued)
This unit continues exploring globalization's impacts and challenges.
What You'll Learn:
- Winners and Losers: Distributional effects of globalization
- Developing Countries: Integration challenges and opportunities
- Anti-Globalization Movements: Critiques and resistance
- Global Value Chains: International production networks
- Future Trends: The evolving global economic order
📘 Unit 14: The 2008 Global Financial Crisis
This unit analyzes the most serious economic crisis since the Great Depression.
What You'll Learn:
- Origins: Subprime mortgage crisis and housing bubble
- Financial Contagion: How crisis spread globally
- Banking Collapse: Lehman Brothers and financial system breakdown
- Great Recession: Economic downturn and unemployment
- Government Responses: Bailouts and stimulus packages
📘 Unit 15: The 2008 Global Financial Crisis (Continued)
This unit explores the aftermath of the crisis and lessons learned.
What You'll Learn:
- Recovery Policies: Monetary and fiscal responses
- Eurozone Crisis: Sovereign debt problems in Europe
- Financial Regulation: Reforms to prevent future crises
- Long-Term Effects: Impact on inequality and economic growth
- Comparative Analysis: 1929 vs. 2008 – similarities and differences
📊 Learning Path
The course follows a chronological progression:
🗓️ Weeks 1-2: Foundation (Unit 1)
🗓️ Weeks 3-5: The Great Depression (Units 2-3)
🗓️ Weeks 6-7: Industrial Revolution (Units 4-5)
🗓️ Weeks 8-9: Post-WWII Economic Systems (Units 6-7)
🗓️ Weeks 10-11: Bretton Woods & International Order (Units 8-9)
🗓️ Week 12: Collapse of Socialism (Unit 10)
🗓️ Week 13: Rise of Asia (Unit 11)
🗓️ Weeks 14-15: Globalization (Units 12-13)
🗓️ Weeks 16-17: 2008 Crisis (Units 14-15)
✅ What to Expect in Each Unit:
Every unit includes:
📄 PDF Lecture Notes – Comprehensive written materials
📊 PowerPoint Presentation – Visual summaries and key points
🎥 Video Resources – Documentaries and educational videos
📖 Glossary – Key terms and definitions
📚 Required Readings – Academic articles and textbook chapters
💬 Discussion Forum – Weekly discussion questions
✅ Self-Check Quiz – Practice questions (unlimited attempts)
📝 Assignments – Written tasks and projects
🎯 How to Succeed:
✓ Complete readings before each lecture
✓ Participate actively in discussions
✓ Review glossary terms regularly
✓ Watch recommended videos
✓ Complete all quizzes and assignments
✓ Ask questions in the forum
✓ Attend live sessions
✓ Connect historical events to current economic issues
Navigate through the units progressively, engage with the materials, and don't hesitate to ask questions!
Dr. Hassiba Almi
📧 hassibali090@gmail.com
📝 Prerequisite Self-Assessment Quiz
Before You Start
Dear Students,
This quiz helps you check if you're ready for History of Economic Facts.
You should know:
- Basic economic concepts (GDP, inflation, supply/demand)
- Economic systems (capitalism, socialism)
- Major 20th-century historical events
- Simple cause-and-effect analysis
⚠️ Don't worry! This is practice only - unlimited attempts, doesn't count toward your grade.
Take this quiz to assess your preparation level.
🎯 Quiz Settings
- Questions: 13
- Time: 30 minutes
- Attempts: Unlimited
- Passing: 60% (9/15)
- Grade: Does NOT count
✅ Results Guide
80-100%: Excellent! Ready to start ✅
60-79%: Good! Review weak areas 📖
Below 60%: Review and retake 🔄Remember: This helps YOU succeed!